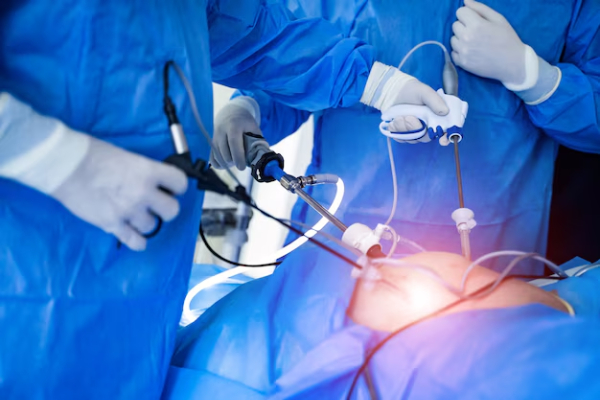
Laparoscopic surgery, also known as minimally invasive surgery (MIS) or keyhole surgery, is a modern surgical technique that uses small incisions and a laparoscope (a thin tube with a camera and light) to perform procedures inside the abdomen and pelvis. This method is less invasive than traditional open surgery, leading to faster recovery, less pain, and reduced scarring.
Common Laparoscopic Procedures
1. General & Abdominal Surgery
2. Gynecological Surgery
3. Urological Surgery
4. Weight Loss (Bariatric) Surgery
How Laparoscopic Surgery Works
- Anesthesia – The patient is given general anesthesia.
- Small Incisions – Tiny cuts are made in the abdomen.
- Carbon Dioxide Inflation – The abdomen is filled with gas for better visibility.
- Insertion of the Laparoscope – A camera provides a high-definition view inside the body.
- Surgical Instruments Used – Miniature tools are inserted through small incisions to perform the surgery.
- Closure – The instruments are removed, and the small incisions are closed with stitches or surgical glue.